|
 |
| J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg > Volume 17(2); 2015 > Article |
|
Abstract
Before the advent of endovascular coiling, patients with multiple intracranial aneurysms were treated with surgical clipping; however, with the advancements in endovascular technology, intracranial aneurysms can be treated with surgical clipping and/or endovascular coiling. We describe a case of subarachnoid hemorrhage in a patient with 7 intracranial aneurysms. A 45-year-old female developed a sudden headache and left sided hemiparesis. Initial workup showed a subarachnoid hemorrhage in the right Sylvian fissure. Further angiographic workup showed 7 intracranial aneurysms (left and right middle cerebral artery bifurcation, right middle cerebral artery, anterior communicating artery, left posterior communicating artery, right posterior inferior cerebellar artery, and left superior cerebellar artery). The patient underwent two craniotomies for surgical clipping of the anterior circulation aneurysms and endovascular stent-assisted coils for the posterior circulation aneurysms. The need for anti-platelet agents for endovascular treatment of the posterior circulation aneurysms and clinical presentation warranted surgical clipping of the anterior circulation aneurysms prior to endovascular therapy. We describe a case report and decision making for a patient with multiple intracranial aneurysms treated with surgical clipping and endovascular coiling.
The prevalence of intracranial aneurysms in the general population is approximately 2%.10)14)19) Intracranial aneurysms can cause subarachnoid hemorrhage, resulting in morbidity of 8-20% and mortality of 37-57%.22) Multiple intracranial aneurysms occur in 7% to 34% of patients with intracranial aneurysms.24) Before the advent of endovascular coiling, patients with multiple intracranial aneurysms were treated with surgical clipping, sometimes requiring multiple craniotomies. With the advancements in endovascular technology, intracranial aneurysms can be treated with surgical clipping and/or endovascular coiling.
Several reports have described treatment of multiple intracranial aneurysms in a 1-stage surgical clipping or coiling.8)11)13)20)21)24)25)26)27)30) In patients with multiple intracranial aneurysms and subarachnoid hemorrhage, when to treat the ruptured aneurysm, if/when to treat the unruptured aneurysms, and which treatment modality best suits the situation must be decided. With clipping or coiling as viable treatment options, deciding which treatment provides the best option for the patient requires a multidisciplinary approach between the endovascular and surgical team. We report on a patient who presented with subarachnoid hemorrhage and was found to have 7 intracranial aneurysms. We describe our multimodality management with clipping and coiling. To the best of our knowledge, there is no report discussing the treatment algorithm in a patient with seven intracranial aneurysms.
A 45-year-old African-American female presented to an outside hospital with an acute headache associated with nausea and left sided hemiparesis. She reported that the headache had started 3 weeks ago and progressively worsened following a bowel movement. She denied loss of consciousness, seizures, incontinence, paresthesia, chest pain, shortness of breath, and orthopnea. Her past medical history was significant for hypertension and smoking. Computed tomography (CT) angiography performed at the outside facility demonstrated possible aneurysms and she was transferred to our tertiary care center for a higher level of care. Upon arrival, her Glascow Coma Scale (GCS) was 15 with stable vitals. Her neurologic examination was unremarkable except for a slight decrease in motor strength (4/5) on the left side.
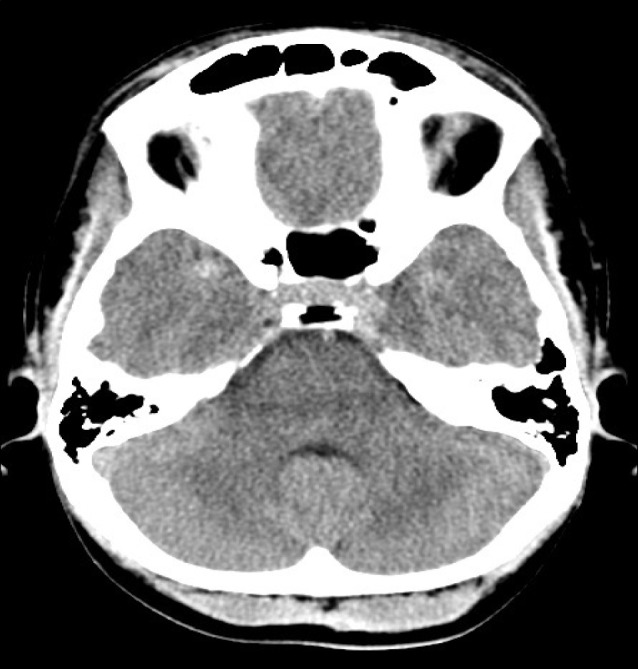
A CT scan showed a subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) located in the right Sylvian fissure (Fig. 1). CT angiogram demonstrated concomitant multiple intracranial aneurysms. Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) showed a total of 7 intracranial aneurysms (Fig. 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8). The angiogram showed right middle cerebral artery (M1) and middle cerebral artery (MCA) bifurcation aneurysm, left MCA bifurcation aneurysm, left posterior communicating artery (PCOM) aneurysm, anterior communicating artery (ACOM) aneurysm (filling from both the right and left carotid injections), left superior cerebellar artery (SCA) and a right posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) aneurysm.
Considering the extraordinary number of intracranial aneurysms seen in our patient, a multidisciplinary approach to management of these aneurysms was considered. After consultation with the neurointerventionalist, it was determined that a stent-assisted coil would be required for endovascular treatment of the MCA aneurysms and the SCA aneurysm. Because of the risk of complications with endovascular treatment of MCA aneurysms, we elected to clip the ruptured aneurysm and the remaining anterior circulation aneurysms. The patient underwent a right pterional craniotomy for microsurgical clipping of the two MCA aneurysms on the right side. Two months later, the patient underwent a left pterional craniotomy for clipping of the left MCA artery aneurysm, left PCOM aneurysm, and the ACOM aneurysm (Fig. 9). Finally, the patient underwent stent assisted coil embolization of the left SCA aneurysm and coil embolization of the right PICA aneurysm two months later (Fig. 10).
The inpatient stay was uneventful for all surgical/endovascular interventions. Following surgical clipping of the right sided MCA aneurysm, her left sided hemiparesis improved post-operatively and had completely resolved at the time of discharge one week post-surgery. The post-operative imaging showed complete occlusion of all seven intracranial aneurysms.
Surgical clipping and endovascular coiling are the two main treatment modalities for intracranial aneurysms. Different combinations of treatment modalities can be used in cases of multiple aneurysms. Using our institutional protocol, the neurosurgeon has the first right-of-refusal. In general, all posterior circulation aneurysms are treated endovascularly. With anterior circulation aneurysms, older patients are treated endovascularly while younger patients are treated with surgical clipping. In this particular case, because the life expectancy was longer than the longevity of coiling and inherent risks of treating MCA aneurysms endovascularly, we elected to clip the anterior circulation aneurysms first. Because treatment of the SCA aneurysm would involve a stent, clipping the anterior circulation aneurysms first would avoid having to stop anti-platelet agents for surgery.
Many surgeons advocate for early treatment of ruptured aneurysms to prevent rebleeding and vasospasm.3)4)6)16)17)28) More importantly, the risk of subarachnoid hemorrhage in coexisting aneurysms is higher.2) As a result, treatment of multiple coexisting aneurysms is recommended.6)7)29) We decided on prompt treatment of the ruptured aneurysm and unruptured aneurysms due to the aforementioned reasons.
Several reports have debated a 1-stage treatment versus a staged procedure. With endovascular coiling, staging treatments avoids multiple craniotomies, thus decreasing the morbidity and mortality from invasive surgery. In this case, due to the diverse nature of the pathology, treatment of all seven intracranial aneurysms required a staged multidisciplinary approach including both clipping and coiling. According to previous reports, surgical clipping of multiple aneurysms can lead to poorer outcomes; however, because multiple aneurysms were accessible with one craniotomy, manipulation of brain tissue was minimized in order to avoid postoperative deficits or complications.11)20)21)24)27)
Risk factors for subarachnoid hemorrhage include cigarette smoking, hypertension, and heavy daily caffeine intake.12)15) Risk factors for multiple intracranial aneurysms include female gender, smoking, hypertension, and family history of cerebrovascular disease, all of which were present in our case.5)23) Other risk factors such as atherosclerosis, use of oral contraceptives, type III collagen abnormality, asymmetry of circle of Willis, arteriovenous malformations, viral infections, and pituitary tumors have contributed to aneurysm formation but may not necessarily contribute to multiple intracranial aneurysm formation.27)29) Genetic risk factors that could have predisposed this patient were not investigated by the authors.
In a retrospective examination of 124 patients with multiple intracranial aneurysms by Imhof and Yonekawa, 18 patients had 4 or more aneurysms, but it did not state the maximum number of intracranial aneurysms encountered in a single patient. The authors examined 1-stage clipping versus a staged treatment and found that the Glasgow Outcome Score between the two groups was the same.9) In our case, a staged procedure was warranted due to aneurysms located in the anterior and posterior circulation and the acute need for treating the ruptured aneurysm.
Baumann et al. retrospectively analyzed 99 patients who underwent surgery for multiple intracranial aneurysms. The authors found female predominance (3:1) and smoking as the most prevalent risk factors. The most prevalent location for an aneurysm in these multiple cases was the MCA bifurcation (27%), followed by ACOM (18%), then the MCA-M1 (6.5%). The most prevalent location of rupture was the ACOM (35%), followed by MCA bifurcation (22%), PCOM (13%), and MCA-M1 (7%).1) In our case, all of these locations harbored aneurysms, and the ruptured aneurysm was located at the MCA-bifurcation.
Several papers reporting on treatment of multiple aneurysms discuss surgical clipping, not a combined clipping and coiling approach. One of the largest reports in the literature discussing dual treatment modality is from Lawton et al.18) Of the 491 patients treated surgically, 77 patients required a multimodal treatment. The authors describe complicated cases that required a wide variety of surgical and endovascular treatments. Thirteen patients were described as having multiple aneurysms that required clipping and coiling. The impetus for dual treatment modality in this subset of patients was mainly to avoid an additional craniotomy. There was no discussion of a treatment algorithm for complicated cases with multiple aneurysms or how the need for anti-platelet agents can alter management.18)
In a patient with multiple aneurysms and two available treatment options, one must consider which aneurysms to treat, how many stages, how quickly to treat, and the treatment modality. The possible need for stenting and, thus, anti-platelet agents should be discussed prior to any treatment.
Several reports discuss patients with multiple intracranial aneurysms; however, none specifically describe a multimodality treatment algorithm for seven intracranial aneurysms. More importantly, decisions regarding which aneurysm to treat first and which modality to use play a critical role. We describe a complicated case of seven intracranial aneurysms, our treatment algorithm, and the use of both surgical clipping and endovascular coiling.
References
1. Baumann F, Khan N, Yonekawa Y. Patient and aneurysm characteristics in multiple intracranial aneurysms. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2008 103:19-28;


2. Bederson JB, Awad IA, Wiebers DO, Piepgras D, Haley EC Jr, Brott T, et al. Recommendations for the management of patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms: A Statement for healthcare professionals from the Stroke Council of the American Heart Association. Stroke. 2000 11;31(11):2742-2750;


3. Chyatte D, Fode NC, Sundt TM Jr. Early versus late intracranial aneurysm surgery in subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 1988 9;69(3):326-331;


4. de Gans K, Nieuwkamp DJ, Rinkel GJ, Algra A. Timing of aneurysm surgery in subarachnoid hemorrhage: a systematic review of the literature. Neurosurgery. 2002 2;50(2):336-342; discussion 340-2


5. Ellamushi HE, Grieve JP, Jager HR, Kitchen ND. Risk factors for the formation of multiple intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 2001 5;94(5):728-732;


6. Findlay JM. Current management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage guidelines from the Canadian Neurosurgical Society. Can J Neurol Sci. 1997 5;24(2):161-170;


7. Heiskanen O. Risk of rebleeding from unruptured aneurysm in cases with multiple intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 1981 10;55(4):524-526;


8. Hong T, Wang Y. Unilateral approach to clip bilateral multiple intracranial aneurysms. Surg Neurol. 2009 8;72(Suppl 1):S23-S28;


9. Imhof HG, Yonekawa Y. Management of ruptured aneurysms combined with coexisting aneurysms. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2005 94:93-96;


10. Inagawa T, Hirano A. Autopsy study of unruptured incidental intracranial aneurysms. Surg Neurol. 1990 12;34(6):361-365;


11. Inagawa T. Surgical treatment of multiple intracranial aneurysms. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1991 Jan-Feb;108(1-2):22-29;


12. Isaksen J, Egge A, Waterloo K, Romner B, Ingebrigtsen T. Risk factors for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: the Tromso study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2002 8;73(2):185-187;



13. Jeon P, Kim BM, Kim DJ, Kim DI, Suh SH. Treatment of multiple intracranial aneurysms with 1-stage coiling. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014 6;35(6):1170-1173;



14. Juvela S, Porras M, Heiskanen O. Natural history of unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a long-term follow-up study. J Neurosurg. 1993 8;79(2):174-182;


15. Juvela S. Prevalence of risk factors in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage and aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Arch Neurol. 1996 8;53(8):734-740;


16. Kassell NF, Torner JC, Jane JA, Haley EC Jr, Adams HP. The international cooperative study on the timing of aneurysm surgery. Part 2: surgical results. J Neurosurg. 1990 7;73(1):37-47;


17. Laidlaw JD, Siu KH. Ultra-early surgery for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: outcomes for a consecutive series of 391 patients not selected by grade or age. J Neurosurg. 2002 8;97(2):250-258;


18. Lawton MT, Quinones-Hinojosa A, Sanai N, Malek JY, Dowd CF. Combined Microsurgical and Endovascular Management of Complex Intracranial Aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2003 2;52(2):263-274; discussion 274-5


19. McCormick WF, Acosta-Rua GJ. The size of intracranial saccular aneurysms. An autopsy study. J Neurosurg. 1970 10;33(4):422-427;


20. Mizoi K, Suzuki J, Yoshimoto T. Surgical treatment of multiple aneurysms: review of experience with 372 cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1989 Jan-Feb;96(1-2):8-14;


21. Mount LA, Brisma R. Treatment of multiple intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 1971 12;35(6):728-730;


22. Nieuwkamp DJ, Setz LE, Algra A, Linn FH, de Rooij NK, Rinkel GJ. Changes in case fatality of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage over time, according to age, sex, and region: a meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2009 7;8(7):635-642;


23. Qureshi AI, Suarez JI, Parekh PD, Sung G, Geocadin R, Bhardwaj A, et al. Risk factors for multiple intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 1998 7;43(1):22-27;


24. Rinne J, Hernesniemi J, Puranen M, Saari T. Multiple intracranial aneurysms in a defined population: prospective angiographic and clinical study. Neurosurgery. 1994 11;35(5):803-808;


25. Solander S, Ulhoa A, Vinuela F, Duckwiler GR, Gobin YP, Martin NA, et al. Endovascular treatment of multiple intracranial aneurysms by using Guglielmi detachable coils. J Neurosurg. 1999 5;90(5):857-864;


27. Vajda J. Multiple intracranial aneurysms: a high risk condition. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1992 Jan-Feb;118(1-2):59-75;


28. Whitfield PC, Kirkpatrick PJ. Timing of surgery for aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001 (2):CD001697


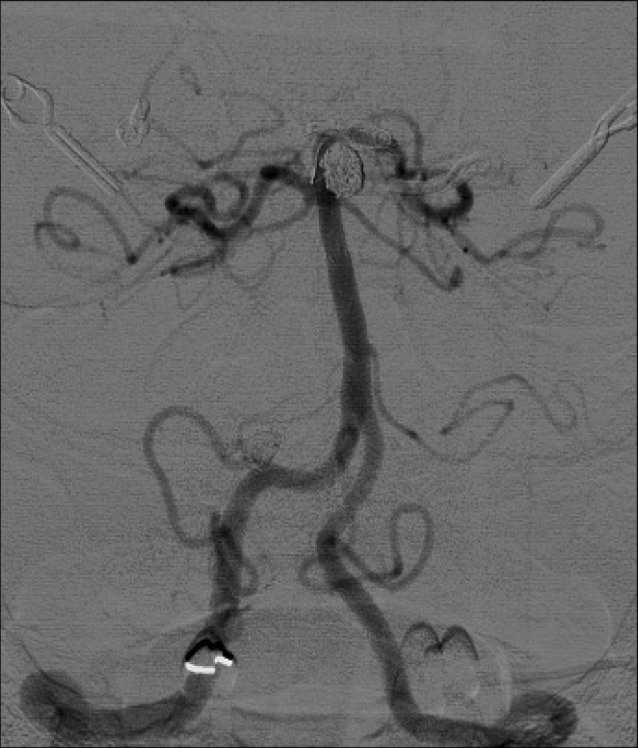
Fig. 2
Anterior-posterior view of a right carotid injection angiogram. From right to left, the first arrow indicates a right-filling anterior communicating artery aneurysm. The second arrow indicates a M1 aneurysm. The third arrow indicates a middle cerebral artery (MCA) bifurcation aneurysm. The MCA bifurcation aneurysm was the suspected ruptured aneurysm based on the clinical presentation.
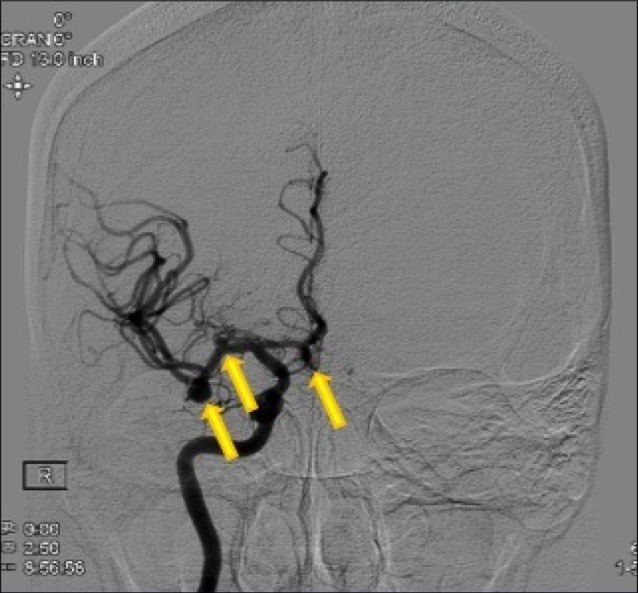
Fig. 3
Anterior-posterior view of a left carotid injection angiogram. The arrow indicates a middle cerebral artery bifurcation aneurysm.
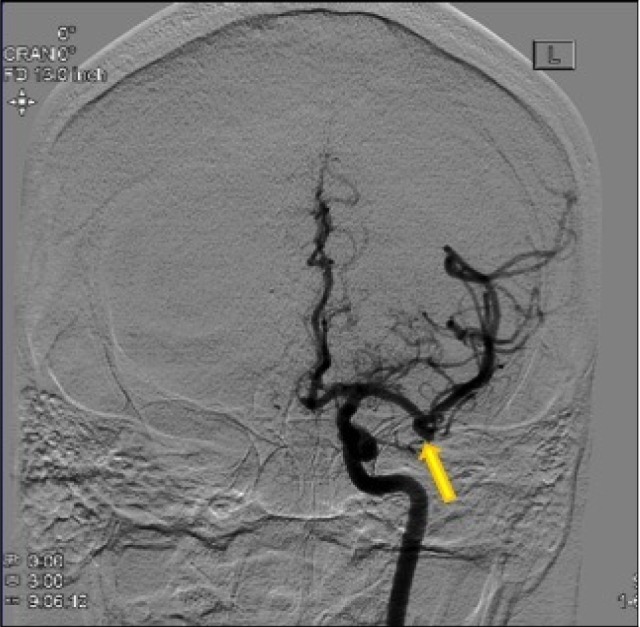
Fig. 4
Lateral view of a left carotid injection angiogram identifying the posterior communicating artery aneurysm.
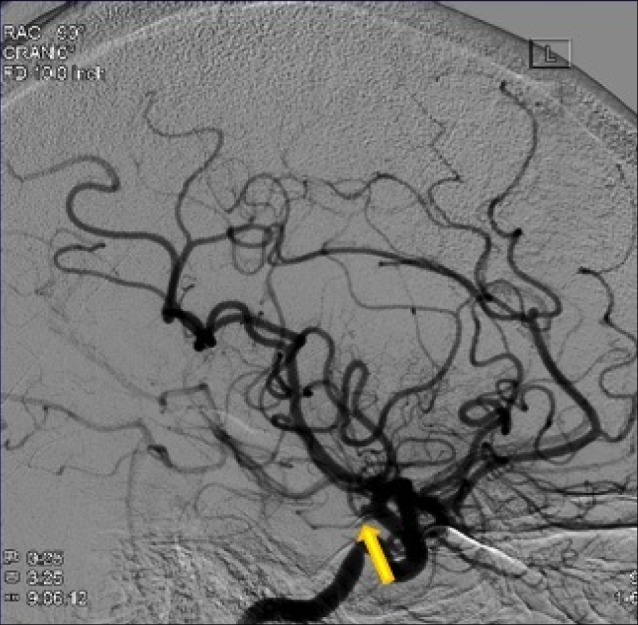
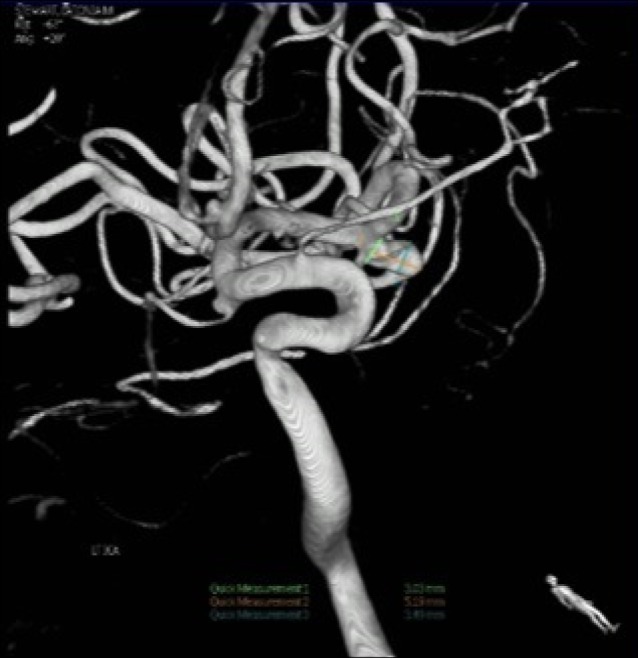
Fig. 5
Anterior-posterior view of a right vertebral injection angiogram showing a right posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysm and a left superior cerebellar artery aneurysm.

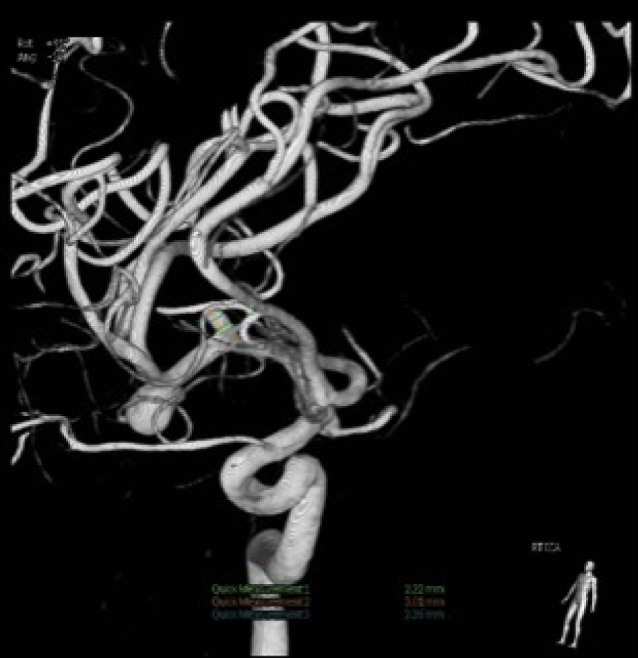
Fig. 8
3D reconstruction of the right vertebral artery. The left superior cerebellar artery has a wide neck, which required a stent-assisted coil and use of anti-platelet agents.

- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 8 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
- 2,753 View
- 17 Download
- Related articles
-
Ruptured mirror DACA aneurysm: A rare case report and review of literature2023 September;25(3)
Intracranial Aneurysm Following Cranial Radiation Therapy2012 December;14(4)




 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print